- Doctors & Departments
-
Conditions & Advice
- Overview
- Conditions and Symptoms
- Symptom Checker
- Parent Resources
- The Connection Journey
- Calm A Crying Baby
- Sports Articles
- Dosage Tables
- Baby Guide
-
Your Visit
- Overview
- Prepare for Your Visit
- Your Overnight Stay
- Send a Cheer Card
- Family and Patient Resources
- Patient Cost Estimate
- Insurance and Financial Resources
- Online Bill Pay
- Medical Records
- Policies and Procedures
- We Ask Because We Care
Click to find the locations nearest youFind locations by region
See all locations -
Community
- Overview
- Addressing the Youth Mental Health Crisis
- Calendar of Events
- Child Health Advocacy
- Community Health
- Community Partners
- Corporate Relations
- Global Health
- Patient Advocacy
- Patient Stories
- Pediatric Affiliations
- Support Children’s Colorado
- Specialty Outreach Clinics
Your Support Matters
Upcoming Events
Child Life 101
Wednesday, June 12, 2024Join us to learn about the work of a child life specialist, including...
-
Research & Innovation
- Overview
- Pediatric Clinical Trials
- Q: Pediatric Health Advances
- Discoveries and Milestones
- Training and Internships
- Academic Affiliation
- Investigator Resources
- Funding Opportunities
- Center For Innovation
- Support Our Research
- Research Areas

It starts with a Q:
For the latest cutting-edge research, innovative collaborations and remarkable discoveries in child health, read stories from across all our areas of study in Q: Advances and Answers in Pediatric Health.


Digestive Health
Constipation and Fecal Soiling (Encopresis)
We specialize in the big things, the small things and everything in between.

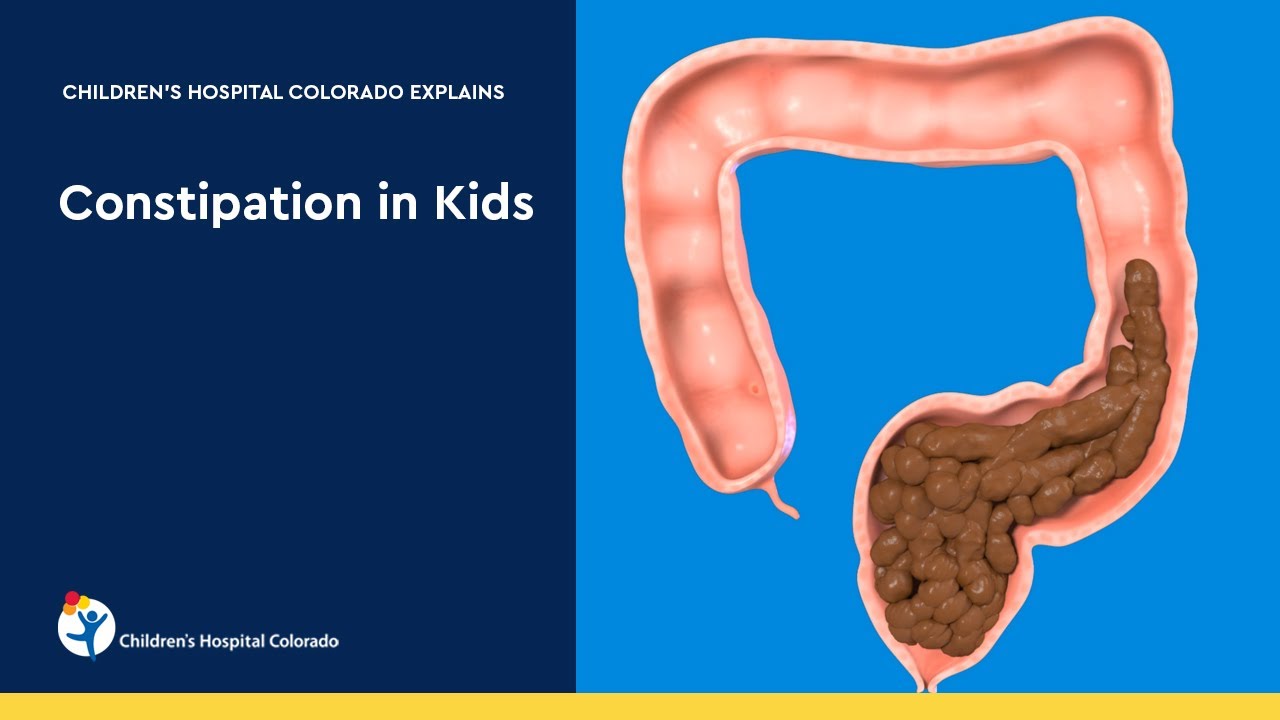
What is constipation and fecal soiling?
Constipation, or the infrequent passage of stools, is a common problem in children. When a constipated child passes stool, it is usually hard and painful from sitting in the rectum for a long time. To avoid passing another painful stool, children will tighten their bottom and withhold stool which sets up a cycle of developing large, hard stools that are painful to pass. For some children, the large intestine fills with hard stool and liquid stool leaks around the hard stool, through the anus and into the child's underwear. This is called fecal soiling, or encopresis.
What causes constipation?
For most children the exact cause of constipation is unknown. Some things that might contribute to constipation include:
- Not drinking enough fluids
- Consuming too much milk and cheese
- Eating a diet that is low in fiber
- Not getting enough exercise
- Playing too hard and ignoring the body's signals to use the restroom
- Too much pressure around potty training
- Avoiding public restrooms
In a few rare cases, constipation might be due to structural, neurologic, endocrine or metabolic disorders.
Fecal soiling is usually a result of constipation which has occurred for a long time or has been difficult to manage. Children with fecal soiling have a large amount of stool in the large intestine, resulting in unintentional soiling accidents. There are a few other cases of fecal soiling such as spinal abnormalities or anorectal abnormalities but these are less common.
Who gets constipation?
Anyone can develop constipation, but it is more common in boys. Common times for constipation to develop are when solid foods are started, around toilet training, birth of a sibling, the start of a new school year, when on vacation or after a time of illness.
What are the signs and symptoms of constipation?
Children who are constipated can show a variety of behavioral and physical symptoms. They include:
- Hiding in the corner, turning red in the face, crying, screaming, shaking and crossing their legs to keep from passing stool. Parents often mistake this behavior as trying to have a bowel movement when in fact the child is trying to withhold a bowel movement.
- Abdominal pain and bloating
- Passage of dry, hard stools
- Skipping days between stools
- Passage of stool that clogs the toilet
- Passage of stool that causes a tear in the anus called a fissure. Blood is usually seen on the toilet tissue.
- An appetite that varies between being very small to very large
- Leakage of stool in the underwear (sometimes this is mistaken for diarrhea)
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
What tests are used to diagnose constipation and fecal soiling?
In most cases, constipation and fecal soiling can be diagnosed after a health care provider completes a detailed history and physical examination. Occasionally other tests might be needed. These may include:
- Blood work
- Abdominal X-ray
- Barium enema
- Rectal biopsy
How do providers at Children’s Hospital Colorado make a diagnosis?
A diagnosis can usually be made at the first visit after a complete health history and physical examination.
How is constipation and fecal soiling treated?
The focus of treatment for children with constipation is changing the child's behavior and making sure the child is not afraid of having a bowel movement. If necessary, diet changes are also made, sometimes with the help of a registered dietitian. Often medications are used for a period of time to help retrain the bowel. Generally a combination of medications are used which may include stool softeners, stimulants, enemas or suppositories to remove any impacted stool and help a child have more regular bowel movements.
For the child with fecal soiling, treatment is more extensive. It often begins with a bowel cleanout followed by a program that is designed to empty the colon on a daily basis. For some children, the colon has been stretched out and it can take up to a year before it regains its original size and shape. Most children respond well to treatment and after a period of rehabilitation have normal bowel movements without soiling.
Why choose Children's Hospital Colorado for your child's constipation?
The treatment for children with fecal soiling requires sensitivity to the child's emotional needs. Children are often embarrassed and do not feel comfortable talking about their stool problem. Providers at Children's Colorado are skilled at communicating with children around sensitive matters. Learn more about the Digestive Health Institute.
- Gastrokids.org (established by the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition)
- National Digestive Disease Information Clearinghouse
- International Foundation for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders
Next steps
-
Would you like to learn more about us?
Learn more about the Digestive Health Institute -
Do you have questions about your child’s condition?
720-777-6669 -
Want a second opinion?
Get started

Compassionate care, wherever you are
We’re here when you need us. Telehealth appointments are available across every specialty, so you can get the high-quality care we’ve always offered from the comfort, privacy and convenience of home.
See if telehealth is right for you
Get to know our pediatric experts.

Laura Quinn, MD
Gastroenterology - Pediatric, Pediatrics

Stephanie Petersburg, PA-C
Physician Assistant

Samantha Woodruff, MD
Gastroenterology - Pediatric

Sarah Kinder, MD
Gastroenterology - Pediatric



 720-777-0123
720-777-0123